Page 52 - English isu 43
P. 52
financial crisis of 2009. On the other hand, weak product prices since
2014 have deeply impacted the price of African exports to China, even
while Chinese exports to Africa remained stable.
great level infrastructural and mining projects. Chinese firms involved in
extractive industries like hydrocarbons that are responsible for the
recovery and exploration of oil and natural gas assets.
The do business between China and Africa surged from $3 billion
in 1995 to $32 billion in 2005 and about $55 billion in 2007, even though
( 31(
Africa makes up only 2.3 per cent of China’s totally trade .
China's strategic integration inputs in Africa are mainly notable in
Ghzlan Mahmoud Abdul Aziz
Figure 2: China’s Trade with Africa (in $ billions)
Figure 2: China’s Trade with Africa (in $ billions)
160
140
120
100
80
China's imports
60 China's exports
40
20
0
1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Source; Johns Hopkins SAIS China Africa research initiative
Source; Johns Hopkins SAIS China Africa research initiative
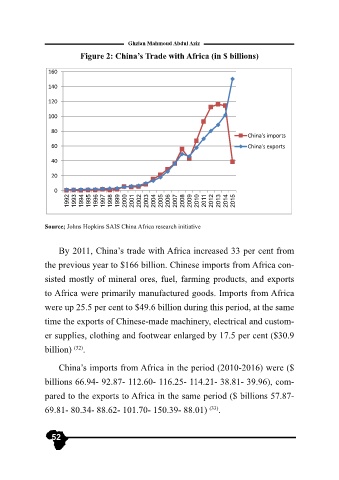
By 2011, China’s trade with Africa increased 33 per cent from
14
~
~
the previous year to $166 billion. Chinese imports from Africa con-
sisted mostly of mineral ores, fuel, farming products, and exports
to Africa were primarily manufactured goods. Imports from Africa
were up 25.5 per cent to $49.6 billion during this period, at the same
time the exports of Chinese-made machinery, electrical and custom-
er supplies, clothing and footwear enlarged by 17.5 per cent ($30.9
billion) .
(32)
China’s imports from Africa in the period (2010-2016) were ($
billions 66.94- 92.87- 112.60- 116.25- 114.21- 38.81- 39.96), com-
pared to the exports to Africa in the same period ($ billions 57.87-
69.81- 80.34- 88.62- 101.70- 150.39- 88.01) .
(33)
52